HasManyThrough relations
- 简介
- 定义 hasManyThrough 关系
- 定义外键属性
- keyThrough in JSON
- Self through
- 方法加入到模型
简介
一个 hasManyThrough 关系设置 many-to-many(多对多)的关系关联到另外的 model, 这个关系表示该声明模型可与另一模型的零个或多个实例通过第三个模型继续进行匹配, 例如,在一个医疗实践,病人预约看医生的申请,相关关系的声明可能是:
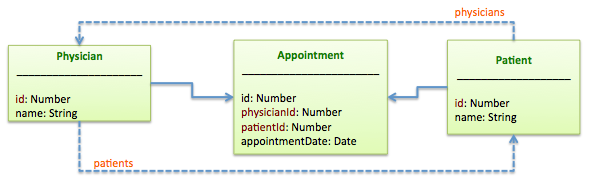
- physician: 医生
- appointment: 任用
- Patient: 患者
The "through(穿透)" model, Appointment 拥有两个外键, physicianId 和 patientId, 引用该主键在声明模型, 医生和目标模式病人。
Defining a hasManyThrough relation
使用 slc loopback:relation 创建两个 Model 之间的联系, 工具会提示你输入模型,相关模型的名称,以及其他必要信息, 然后工具将会修改模型定义文件common/models/modelName.json
案例:common/models/physician.json
{
"name": "Physician",
"base": "PersistedModel",
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"validations": [],
"relations": {
"patients": {
"type": "hasMany",
"model": "Patient",
"foreignKey": "physicianId",
"through": "Appointment"
}
}
}
common/models/patient.json
{
"name": "Patient",
"base": "PersistedModel",
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"validations": [],
"relations": {
"physicans": {
"type": "hasMany",
"model": "Physician",
"foreignKey": "patientId",
"through": "Appointment"
}
}
}
common/models/appointment.json
{
"name": "Appointment",
"base": "PersistedModel",
"properties": {
"appointmentDate": {
"type": "date"
}
},
"validations": [],
"relations": {
"physician": {
"type": "belongsTo",
"model": "Physician",
"foreignKey": "physicianId"
},
"patient": {
"type": "belongsTo",
"model": "Patient",
"foreignKey": "patientId"
}
}
}
定义外键属性
与hasMany 规则一样
keyThrough in JSON
这里是限定与外键一个hasManyThrough关系的一个例子
- 学生(ID,STUNAME):学生信息
- 课程(ID,COURNAME):课程信息
- COURSTU(COURID,STUID):表与处理许多一对多映射外键
common/models/courses.json:
...
"relations": {
"students": {
"type": "hasMany",
"model": "Students",
"foreignKey": "courid",
"through": "Courstu",
"keyThrough": "stuid"
}
...
common/models/students.json:
"relations": {
"courses": {
"type": "hasMany",
"model": "Courses",
"foreignKey": "stuid",
"through": "Courstu",
"keyThrough": "courid"
}
Self through
在某些情况下,你可能要定义从模型关系到自身的 model,
例如,考虑一个社交媒体应用程序,用户可以跟随其他用户。在这种情况下,用户可以按照许多其它用户,并且可以随后许多其它用户。下面的代码显示了这一可能被定义,相应沿keyThrough属性:
User.hasMany(User, {as: 'followers', foreignKey: 'followeeId', keyThrough: 'followerId', through: Follow});
User.hasMany(User, {as: 'following', foreignKey: 'followerId', keyThrough: 'followeeId', through: Follow});
Follow.belongsTo(User, {as: 'follower'});
Follow.belongsTo(User, {as: 'followee'});
方法添加到 Model
一旦定义一个“hasManyThrough”的关系, Loopback 自动添加方法与关系名的声明模型类的原型.
例如: physician.patients.create(...)
| 实例案例 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| physician.patients(filter, function(err, patients) {}) | 发现患者的医师。 |
| var patient = physician.patients.build(data) | 创建一个新的病人 |
| physician.patients.create(data, function(err, patient) { }); | 创建用于医师新患者 |
| physician.patients.destroyAll(function(err) { }); | 删除所有患者医生 |
| physician.patients.add(patient, function(err, patient) { }) | 一个病人添加到医师 |
| physician.patients.remove(patient, function(err) { }) | 取下医生的病人 |
| physician.patients.findById(patientId, function(err, patient) { }) | 查找ID的患者 |
这些关系的方法提供给相关的 Model 使用(如患者在上面的例子). 然而,他们不允许你在一个单一的电话访问这两个相关对象(患者)和“到”的记录(预约)
例如, 如果你想添加一个患者 以及 创建一个 appointment 带上日期, 你必须做出两次调用 (REST requests):
第一步, 通过 Patient.create 创建一个病人
POST /patients
{
"name": "Jane Smith"
}
第二步, 通过 Appointment.create 创建 appointment, 设置 patientId 属性 为 新建的patients.
POST /appointments
{
"patientId": 1,
"physicianId": 1,
"appointmentDate": "2014-06-01"
}
下面的查询可用于列出一个给定的医生所有的患者,包括他们的就诊日期:
GET /appointments?filter={"include":["patient"],"where":{"physicianId":2}}
响应案例:
[
{
"appointmentDate": "2014-06-01",
"id": 1,
"patientId": 1,
"physicianId": 1,
"patient": {
"name": "Jane Smith",
"id": 1
}
}
]